No products in the cart.
7 in 1 Soil PH NPK EC Temperature Humidity Sensor Module with RS485 TTL module
₹7,000.00₹8,000.00 excl GST (-13%)
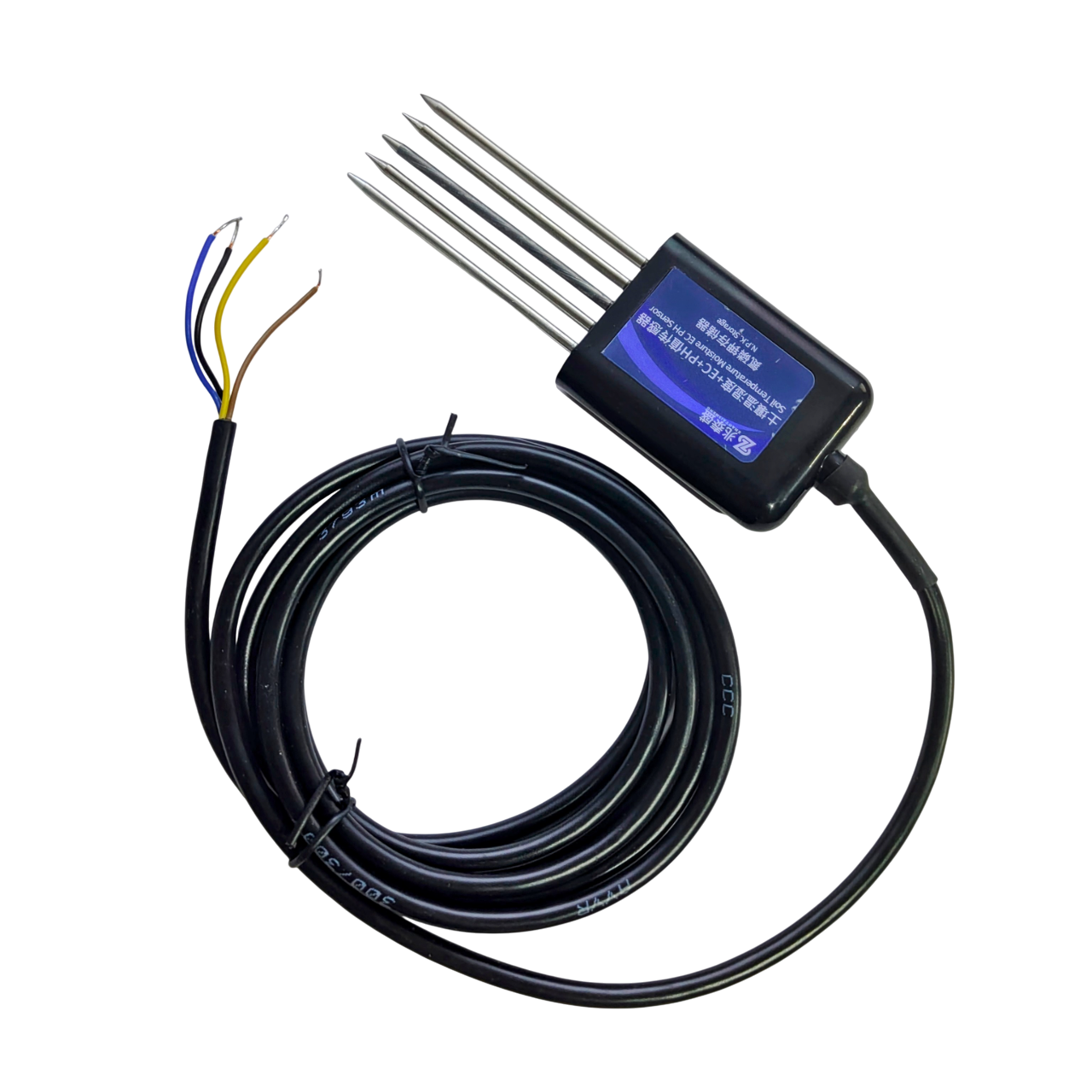
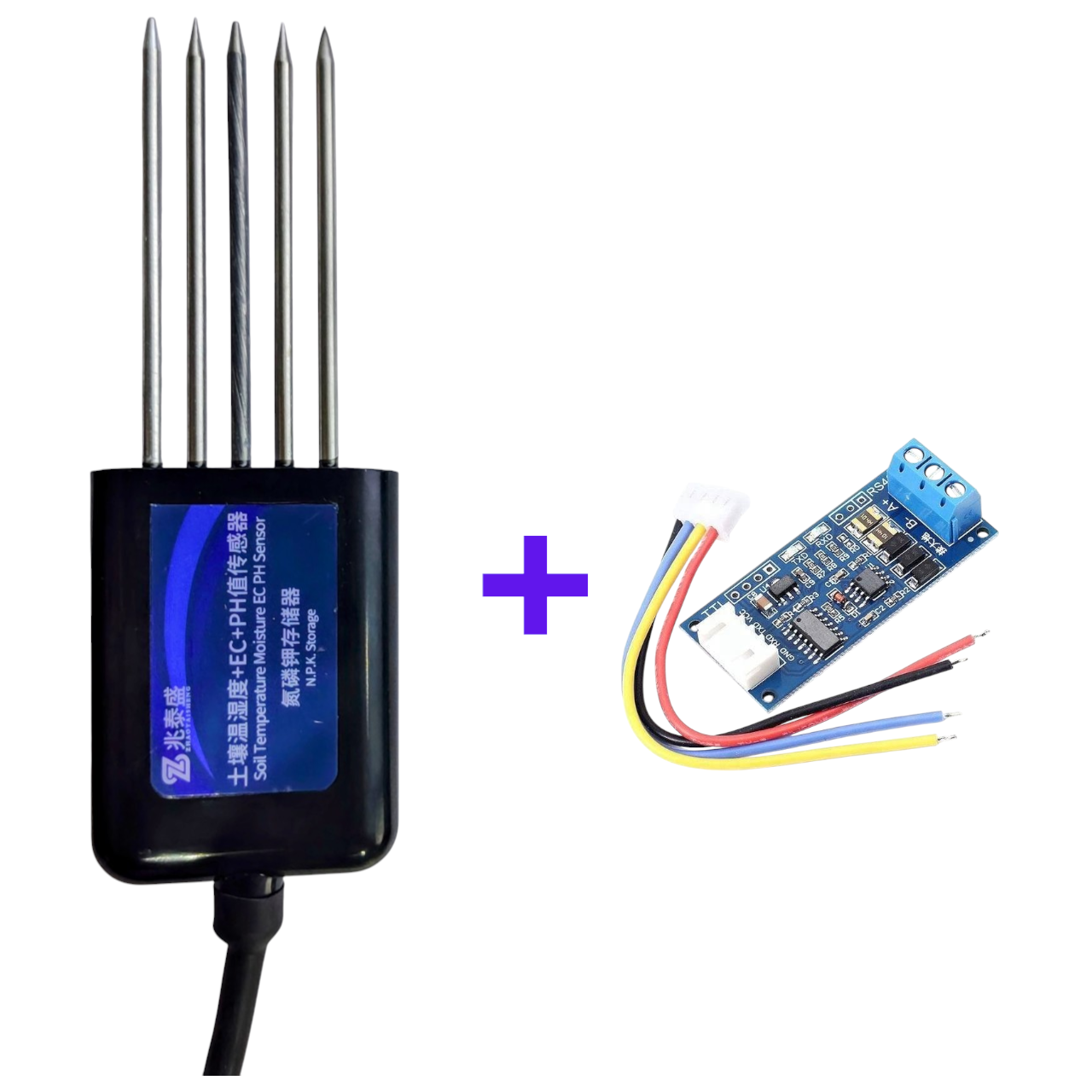
Package Contains: 1 No 5 PIN Soil Multi Parameter Sensor Soil NPK, EC,pH, Temperature,Moisture Detection Sensor with RS485 Output an RS485TTL module
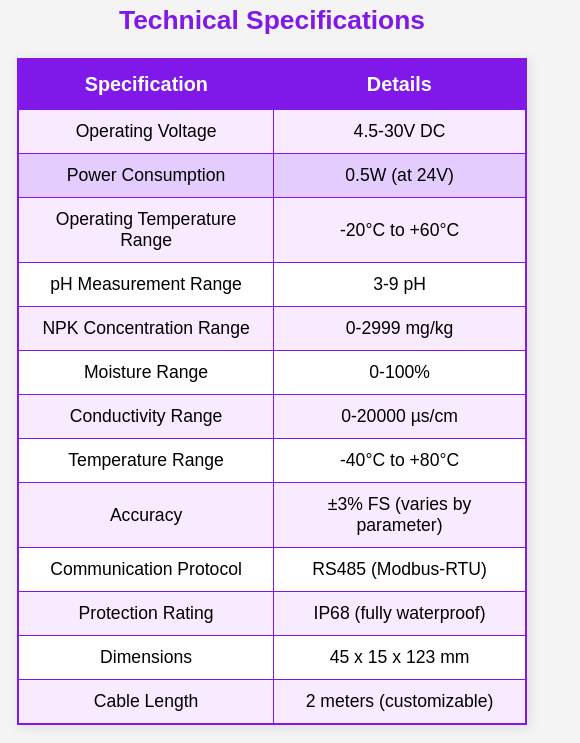
The 7-in-1 Soil NPK Sensor is a cutting-edge multi-parameter soil analysis device designed to provide real-time monitoring of essential soil properties, including pH, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), moisture, temperature, and electrical conductivity (EC). This sensor is ideal for precision agriculture, greenhouse management, environmental monitoring, and scientific research where accurate soil condition assessment is critical.
Connection Diagram:
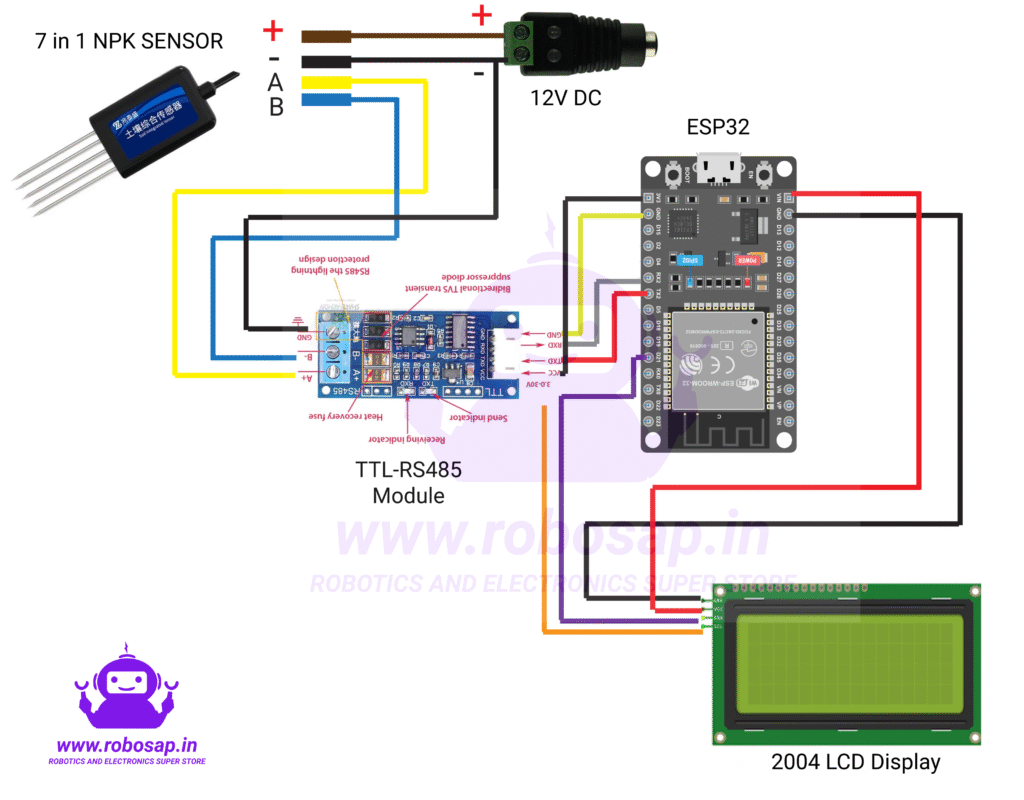
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Soil Analysis: Accurately measures pH, NPK levels, moisture content, temperature, and electrical conductivity to support precision farming and irrigation management.
- High Durability & IP68 Protection: Built with a corrosion-resistant and waterproof IP68-rated structure, ensuring reliable operation in harsh agricultural and environmental conditions.
- Advanced Temperature Compensation: Features an automatic temperature compensation system, ensuring precise conductivity readings even in fluctuating temperature environments.
- Wide Voltage Compatibility: Operates within a 4.5V to 30V DC range, making it suitable for various power supply configurations in agricultural automation systems.
- RS485 Modbus Communication Protocol: Supports RS485 communication using the Modbus-RTU protocol, allowing seamless integration with PLCs, microcontrollers, and industrial monitoring systems.
- Fast Response & High Accuracy: Delivers real-time, high-precision measurements to facilitate data-driven decision-making for soil management and crop optimization.
- Easy Installation & Versatility: The sensor is compact, lightweight, and designed for both portable and fixed installations, enabling flexible deployment across open fields, greenhouses, research labs, and hydroponic systems.
Applications:
- Precision Agriculture: Optimize fertilization, irrigation, and soil conditioning for improved crop yield.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: Monitor soil moisture and conductivity to enable water-saving irrigation strategies.
- Greenhouse & Hydroponic Farming: Ensure optimal growing conditions with real-time soil health monitoring.
- Environmental & Soil Research: Conduct scientific studies on soil composition, nutrient availability, and environmental impact.
- Land Reclamation & Ecosystem Monitoring: Assess soil recovery and suitability for sustainable cultivation.
It is suitable for electrical conductivity, and PH value testing in soil moisture monitoring, scientific experiments, water-saving irrigation, greenhouses, flowers and vegetables, grassland pastures, soil rapid testing, plant cultivation, sewage treatment, precision agriculture, etc.
Also please note Dry or nutrient poor soil may show zero nitrogen readings because there are insufficient water soluble nitrogen ions (like nitrate or ammonium) available for the sensor to detect. Nitrogen is highly mobile and can quickly leach out or volatilize from the soil, especially in dry or sandy conditions. Without adequate moisture and dissolved nutrients, the sensor cannot register a measurable nitrogen value.
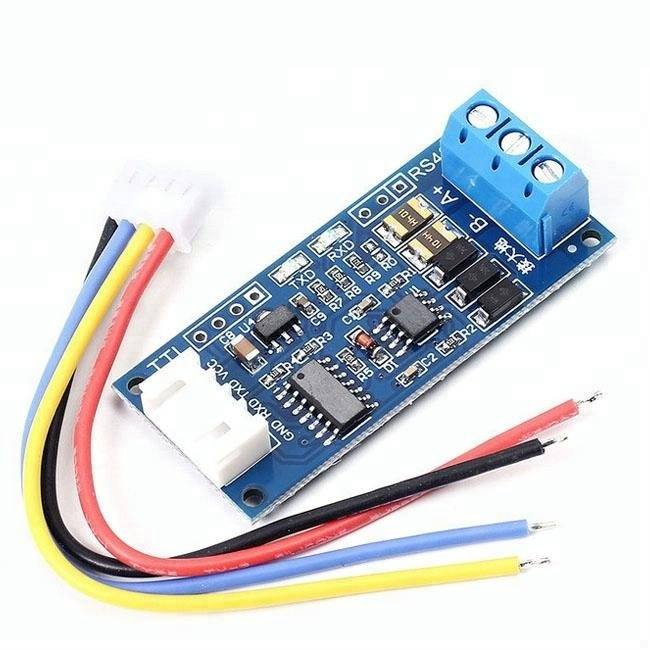
This sensor comes with TTL RS485 Converter Module which is compatible with ESP32 and Raspberry Pi. The TTL to RS485 Module is a high-performance signal conversion device designed to seamlessly convert TTL signals to RS485 and vice versa, ensuring reliable communication between UART-based microcontrollers and RS485 networks. This module supports automatic flow direction control, enabling smooth switching between transmission and reception without manual intervention.
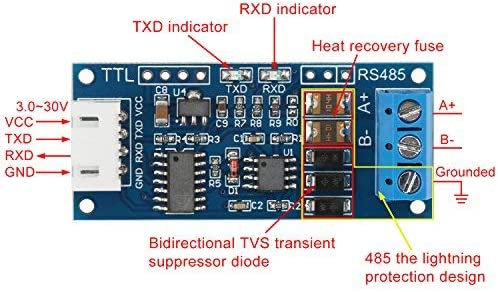
The code for the Above video is given Below:
// Code for 7 in 1 NPK Sensor with 20x4 I2C LCD and Serial Output
// Author: Rohit Kadam, www.robosap.in
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h>
#define RXD2 16
#define TXD2 17
// I2C LCD setup (20 columns, 4 rows, I2C address 0x27)
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 20, 4);
// Modbus request for 7 parameters
unsigned char byteRequest[8] = {0x01, 0x03, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x07, 0x04, 0x08};
unsigned char byteResponse[19] = {};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial2.begin(4800, SERIAL_8N1, RXD2, TXD2);
lcd.init(); // Initialize LCD
lcd.backlight(); // Turn on backlight
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Soil NPK Sensor Init");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
Serial.println("Soil NPK Sensor - Serial Output + LCD");
}
void loop() {
readAndPrintNPK();
delay(5000); // 5 second delay between reads
}
void readAndPrintNPK() {
Serial2.write(byteRequest, sizeof(byteRequest));
delay(1000); // Wait for sensor to respond
if (Serial2.available() >= sizeof(byteResponse)) {
Serial2.readBytes(byteResponse, sizeof(byteResponse));
unsigned int soilHumidity = (byteResponse[3] << 8) | byteResponse[4];
unsigned int soilTemperature = (byteResponse[5] << 8) | byteResponse[6];
unsigned int soilConductivity = (byteResponse[7] << 8) | byteResponse[8];
unsigned int soilPH = (byteResponse[9] << 8) | byteResponse[10];
unsigned int nitrogen = (byteResponse[11] << 8) | byteResponse[12];
unsigned int phosphorus = (byteResponse[13] << 8) | byteResponse[14];
unsigned int potassium = (byteResponse[15] << 8) | byteResponse[16];
// Print to Serial
Serial.println("---- Soil Sensor Readings ----");
Serial.print("Moisture: "); Serial.print(soilHumidity / 10.0); Serial.println(" %");
Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(soilTemperature / 10.0); Serial.println(" °C");
Serial.print("Conductivity: "); Serial.print(soilConductivity); Serial.println(" us/cm");
Serial.print("pH: "); Serial.println(soilPH / 10.0);
Serial.print("Nitrogen: "); Serial.print(nitrogen); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Phosphorus: "); Serial.print(phosphorus); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.print("Potassium: "); Serial.print(potassium); Serial.println(" mg/kg");
Serial.println("--------------------------------\n");
// Print to LCD
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Moist:"); lcd.print(soilHumidity / 10.0); lcd.print("% ");
lcd.print("pH:"); lcd.print(soilPH / 10.0);
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Temp:"); lcd.print(soilTemperature / 10.0); lcd.print("C ");
lcd.print("EC:"); lcd.print(soilConductivity);
lcd.setCursor(0, 2);
lcd.print("N:"); lcd.print(nitrogen); lcd.print(" P:"); lcd.print(phosphorus);
lcd.setCursor(0, 3);
lcd.print("K:"); lcd.print(potassium); lcd.print(" mg/kg");
} else {
Serial.println("No response from NPK sensor.");
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Sensor not ready...");
}
}The Python code is given below:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# 7-in-1 NPK Sensor reader (Modbus RTU) via USB serial on Raspberry Pi
# Author: Rohit Kadam, www.robosap.in
# Notes:
# - Default serial port: /dev/ttyUSB0 (change below if needed)
# - Baud: 4800
import time
import serial
SERIAL_PORT = "/dev/ttyUSB0" # e.g., /dev/ttyUSB0, /dev/ttyUSB1, /dev/ttyAMA0
BAUD = 4800
TIMEOUT = 0.3 # seconds
POLL_MS = 5000
SLAVE_ADDR = 0x01
START_REG = 0x0000
REG_COUNT = 0x0007 # 7 registers → 14 data bytes
# Scaling (adjust if your probe differs)
MOIST_SCALE = 0.1
TEMP_SCALE = 0.1
PH_SCALE = 0.1
EC_SCALE = 1.0 # some probes use 0.1 or 10.0
RESP_LEN = 19 # [addr][func][byteCount=14][14 data][CRCLo][CRCHi]
def crc16_modbus(data: bytes) -> int:
crc = 0xFFFF
for b in data:
crc ^= b
for _ in range(8):
if crc & 0x0001:
crc = (crc >> 1) ^ 0xA001
else:
crc >>= 1
return crc & 0xFFFF
def build_request(slave: int, start_reg: int, reg_count: int) -> bytes:
frame = bytearray(8)
frame[0] = slave
frame[1] = 0x03 # Read Holding Registers
frame[2] = (start_reg >> 8) & 0xFF
frame[3] = start_reg & 0xFF
frame[4] = (reg_count >> 8) & 0xFF
frame[5] = reg_count & 0xFF
crc = crc16_modbus(frame[:6])
frame[6] = crc & 0xFF # CRC Lo
frame[7] = (crc >> 8) & 0xFF # CRC Hi
return bytes(frame)
def read_exact(ser: serial.Serial, n: int, timeout_s: float) -> bytes:
"""Read exactly n bytes or return b'' on timeout."""
deadline = time.time() + timeout_s
out = bytearray()
while len(out) < n and time.time() < deadline:
chunk = ser.read(n - len(out))
if chunk:
out.extend(chunk)
else:
# brief sleep to avoid busy loop if no data
time.sleep(0.001)
return bytes(out) if len(out) == n else b""
def parse_payload(resp: bytes):
"""
resp: 19 bytes total
Indexing:
0 addr, 1 func, 2 byteCount(=14), 3..16 data, 17 crcLo, 18 crcHi
Registers (big-endian) we expect:
0: soilHumidity (×0.1 %)
1: soilTemperature (×0.1 °C)
2: soilConductivity (µS/cm, scale may vary)
3: soilPH (×0.1)
4: nitrogen (mg/kg)
5: phosphorus (mg/kg)
6: potassium (mg/kg)
"""
if len(resp) != RESP_LEN:
raise ValueError("Bad length")
if resp[2] != 14:
raise ValueError("Bad byteCount")
# CRC check
rx_crc = (resp[18] << 8) | resp[17] # Hi:Lo at the end (buffer stores Lo,Hi)
calc_crc = crc16_modbus(resp[:-2])
if rx_crc != calc_crc:
raise ValueError("CRC mismatch")
# Header checks
if resp[0] != SLAVE_ADDR or resp[1] != 0x03:
raise ValueError("Bad addr/func")
# Extract 7 registers (big-endian pairs) from data bytes 3..16
d = resp[3:17]
regs = []
for i in range(0, 14, 2):
regs.append((d[i] << 8) | d[i+1])
soilHumidity = regs[0] * MOIST_SCALE
soilTempC = regs[1] * TEMP_SCALE
soilEC = regs[2] * EC_SCALE
soilPH = regs[3] * PH_SCALE
N, P, K = regs[4], regs[5], regs[6]
return {
"moisture_pct": soilHumidity,
"temperature_c": soilTempC,
"ec_uScm": soilEC,
"ph": soilPH,
"nitrogen_mgkg": N,
"phosphorus_mgkg": P,
"potassium_mgkg": K,
}
def read_once(ser: serial.Serial, retries: int = 3):
req = build_request(SLAVE_ADDR, START_REG, REG_COUNT)
for attempt in range(1, retries + 1):
# flush any stale input
ser.reset_input_buffer()
ser.write(req)
resp = read_exact(ser, RESP_LEN, TIMEOUT)
if not resp:
if attempt == retries:
raise TimeoutError("No/short response from sensor")
continue
try:
return parse_payload(resp)
except Exception as e:
if attempt == retries:
raise
# small inter-attempt delay
time.sleep(0.05)
raise RuntimeError("Unexpected read error")
def main():
print("Soil NPK Sensor - USB Serial Reader (Modbus RTU)")
print(f"Port={SERIAL_PORT}, {BAUD} 8N1, slave=0x{SLAVE_ADDR:02X}")
while True:
try:
with serial.Serial(SERIAL_PORT, BAUD, timeout=0, bytesize=8, parity=serial.PARITY_NONE, stopbits=1) as ser:
while True:
try:
reading = read_once(ser, retries=3)
print("---- Soil Sensor Readings ----")
print(f"Moisture: {reading['moisture_pct']:.1f} %")
print(f"Temperature: {reading['temperature_c']:.1f} °C")
print(f"Conductivity: {reading['ec_uScm']:.1f} uS/cm")
print(f"pH: {reading['ph']:.1f}")
print(f"N: {reading['nitrogen_mgkg']} P: {reading['phosphorus_mgkg']} K: {reading['potassium_mgkg']} (mg/kg)")
print("--------------------------------\n")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[WARN] Read failed: {e}")
time.sleep(POLL_MS / 1000.0)
except serial.SerialException as e:
print(f"[ERROR] Serial open failed on {SERIAL_PORT}: {e}")
print("Retrying in 3s...")
time.sleep(3)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Please Note :
note that the product information provided on our website may not be entirely accurate as it is collected from various sources on the web. While we strive to provide the most up-to-date information possible, we cannot guarantee its accuracy. We recommend that you always read the product labels, warnings, and directions before using any product. Images are for representation only. The actual Product may differ slightly in appearance.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.